Innovation in Organizations
Feb 27, 2024
By Ari Manor , CEO at ZOOZ

This is one in a series of articles that provide detailed and updated information about Innovation.In this specific article, which focuses on Innovation in Organizations, you can read about:
- Why Innovation Management is Important
- Innovation Manager
- Innovation Team
- Innovation Center
- Can Innovation Be a Core Strength of a Firm
- Innovation Culture
- When Innovation Thrives in an Organization
- When Innovations Meet Institutions
- How Can Innovation Be Promoted in an Organization
- What Kills Innovation
- Innovation and its Enemies
- Innovation Jobs
- Innovation Jobs Near Me
- Innovation to Transform Education Training
- Innovation Can Be Increased by
- Innovation Council
- What are the 4 C's of Innovation?
For additional articles about Innovation, see the Topic Menu.

Why Innovation Management is Important
Innovation management is critical because it structures the process of bringing new and creative ideas to life, which is fundamental for any business that seeks to grow, remain competitive, and avoid stagnation.
Why Innovation Management Matters
- Alignment with Strategic Goals: Innovation management ensures that new ideas align with the company's strategic objectives, thereby supporting focused growth and value creation.
- Resource Optimization: By managing innovation, organizations can allocate their resources more effectively, ensuring that the best ideas receive the necessary investment of time and capital.
- Risk Reduction: Innovation management helps to identify potential risks early in the development process, allowing for better risk mitigation and increasing the likelihood of success.
- Market Responsiveness: Effective innovation management enables a company to respond quickly to market changes, customer needs, and technological advancements, keeping it ahead of competitors.
- Culture of Continuous Improvement: It fosters a culture where continuous improvement is valued and sought after, encouraging employees to constantly look for ways to enhance products, services, and processes.
- Sustainable Competitive Advantage: By regularly introducing innovative products, services, or processes, a company can establish and maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
- Attracting and Retaining Talent: A strong focus on innovation attracts talent looking to work in dynamic and forward-thinking environments, and it keeps employees engaged by providing opportunities for creativity and problem-solving.
Applying Systematic Innovation
Innovation management is not just about generating creative ideas; it's about translating those ideas into tangible outcomes that drive business success. It's a discipline that requires coordination, investment, and a strategic approach to harness the creative capabilities of an organization effectively.
Here at ZOOZ Consulting, after leading innovation and strategic processes in hundreds of organizations across many countries, we have developed a methodology for managing all aspects of innovation systematically to reduce risk and improve outcomes. This methodology, known as Systematic Innovation™, incorporates lessons we've learned during our 25 years of experience in the field of business innovation.
The Systematic Innovation methodology includes a comprehensive framework for innovation, as well as highly effective tools, principles, and methods for ongoing innovation management at all stages of the innovation process, as follows:
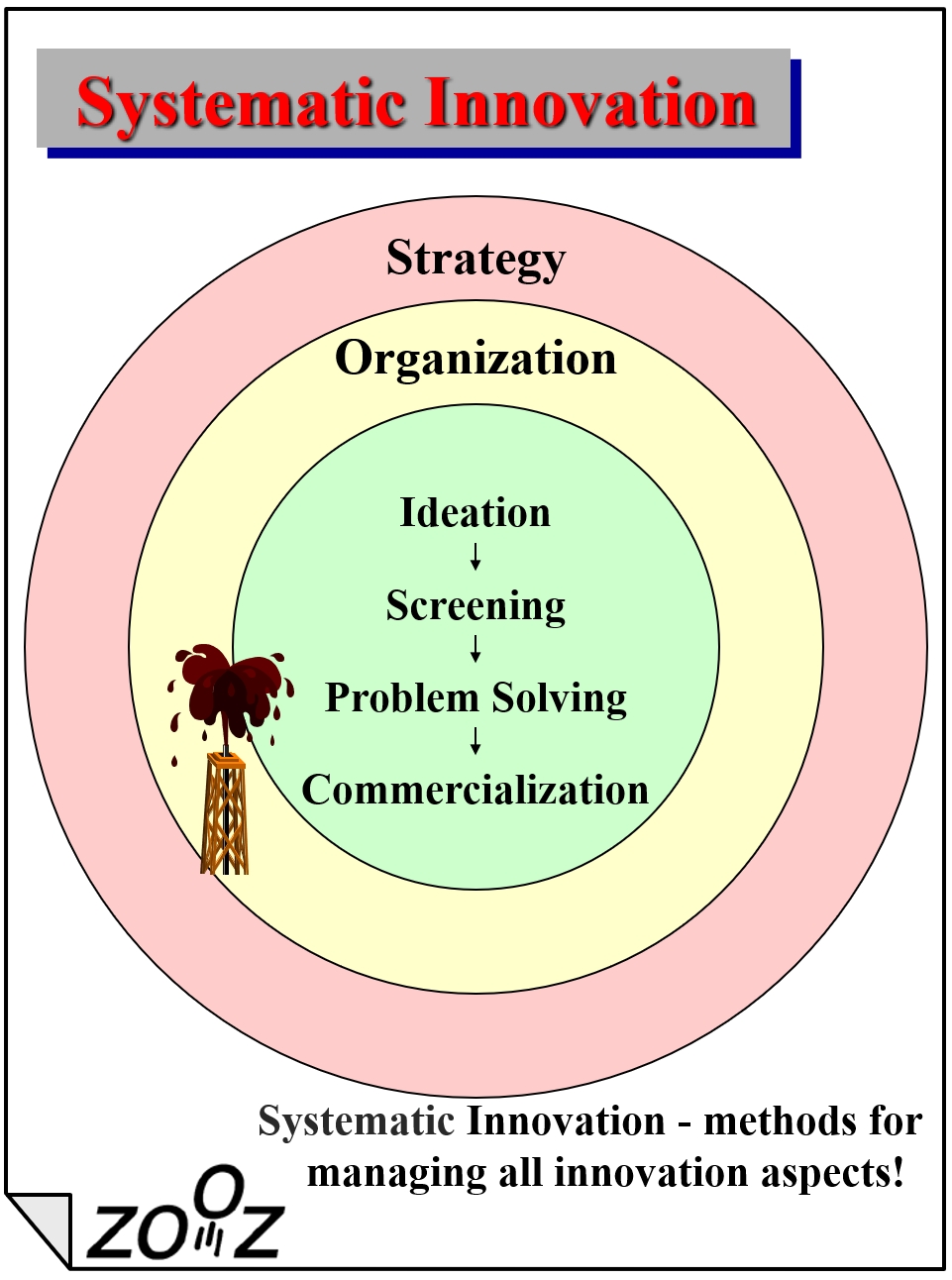 Strategic Infrastructure (a framework for the innovation efforts):
Strategic Infrastructure (a framework for the innovation efforts):- Ensuring there is (or devising) a business strategy that innovation should support.
- Defining a strategy for innovation – goals, innovation focus, fields to innovate in, etc.
- Working on disruptive business strategy – strategic growth paths, blue ocean strategy, etc.
- Organizational Infrastructure (setting up an innovation culture):
- Defining, advancing, and guiding the innovation workforce – Innovation manager, think tanks, etc.
- Providing on-the-job training and nurturing required skills, using systematic tools and methods.
- Offering mass-training to employees to enhance organizational creativity (“Invent in Yourself” Days).
- Assimilating tools to shape an innovation culture (Six thinking hat, Idea Banks, and more)
- Idea Funnel (leading innovation sessions and assimilating dedicated tools and methods):
- Idea generation – we use SIT, SCAMPER, TRIZ, and more, according to the needs.
- Screening – internal screening, external screening via concept testing.
- Problem-solving – using SIT and TRIZ methodologies to overcome technical and logistic issues.
- Commercialization – developing innovative packaging and display solutions, and highly creative ads.
For further detail about Systematic Innovation, read the following articles:
- Building The Future - Insights and recommendations for on innovation management.
- How Do You Make an Organization Innovative? – Organizational aspects of innovation management.
If you need help in applying Systematic Innovation in your organization, contact us.
We offer Systematic Innovation workshops anywhere on the globe.

Innovation Manager
An Innovation Manager plays a pivotal role in steering an organization’s creative capabilities towards strategic business objectives.
The Responsibilities of the Inovation Manager
- Vision and Leadership: Setting the vision for innovation within the company and leading the charge to inspire a culture of continuous improvement and creative thinking.
- Strategy Development: Crafting strategies that align with business goals and determining the best paths for innovation efforts, whether in products, services, processes, or business models.
- Process Management: Overseeing the innovation process from ideation to execution, ensuring that it's efficient, effective, and adheres to the company's strategic direction.
- Collaboration Facilitation: Acting as a liaison between different departments, external partners, and stakeholders to foster collaboration and cross-pollination of ideas.
- Portfolio Management: Managing the portfolio of innovation projects, prioritizing initiatives based on potential impact, and ensuring a balanced mix of incremental and disruptive innovation efforts.
- Resource Allocation: Ensuring that projects have the necessary resources, from funding to expertise, and managing those resources wisely to maximize return on investment.
- Metrics and Analysis: Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) for innovation and analyzing the performance of innovation activities to inform future decisions.
- Change Advocacy: Championing change and helping to overcome resistance by clearly articulating the benefits and value of innovation initiatives.
Innovation Manager Position
- Scope: The position of an Innovation Manager can be either full-time or part-time, depending on the organization's size, industry, and the capacity of innovation activities it undertakes. However, it is essential that this role occupies at least 25% of a full-time position to ensure sufficient attention and momentum is maintained in the innovation process.
- Skills: An Innovation Manager should possess highly analytical skills to manage external screenings and idea banks effectively. Additionally, the innovation manager needs excellent communication and soft skills to navigate organizational barriers, foster a culture of innovation, and motivate team members and peers to engage in innovative activities.
- Size and Type of Organizations: Organizations of all sizes and types can benefit from having an Innovation Manager, especially those in rapidly evolving sectors were staying ahead of technological trends and market demands is critical. While larger corporations may require a dedicated full-time position, smaller firms or startups might start with a part-time role or incorporate these responsibilities into a broader managerial position.
- Experience and Education Required: Typically, an Innovation Manager should have a background in business, management, or a related field, with a bachelor's degree being a minimum requirement. Many also hold advanced degrees such as an MBA or masters in innovation management. Relevant experience in project management, R&D, product development, or strategic planning is crucial. It's also beneficial for Innovation Managers to have a solid understanding of the industry they're working in, along with experience in managing cross-functional teams and implementing change.
In essence, the Innovation Manager's role is to bridge the gap between innovative ideas and their successful implementation, requiring a blend of strategic insight, leadership qualities, and a deep understanding of both market and technological trends, making it one of the most dynamic and influential positions in today's corporate landscape.

Innovation Team
An Innovation Team is a cross-functional group within an organization that is tasked with driving innovation. This team is often composed of individuals from various departments and levels of expertise, bringing diverse perspectives to the table.
Key Functions and Responsibilities of Innovation Teams
- Idea Generation: Brainstorming and developing new ideas that could translate into successful products, services, or processes.
- Prototyping and Testing: Creating prototypes of potential products or models of new services and conducting tests to evaluate feasibility and market potential.
- Market Research: Conducting research to understand market needs, trends, and the competitive landscape to ensure that innovations are relevant and targeted.
- Collaboration: Working with other teams and external partners to develop and refine ideas and bring different skill sets and knowledge bases to the innovation process.
- Project Management: Overseeing innovation projects from conception through to completion, ensuring they meet timelines, budget constraints, and objectives.
- Communication: Keeping all stakeholders informed of the team’s progress, challenges, and successes to maintain transparency and support throughout the organization.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Learning from both successes and failures to continuously improve the innovation process.
Typical Positions in an Innovation Team
- Innovation Manager
- Responsibilities: Oversees the innovation process from ideation to execution, develops innovation strategy aligned with business goals, and fosters a culture of innovation.
- Required Skills: Strong leadership, strategic thinking, project management, and communication skills.
- Education and Experience: Bachelor’s degree in business or related field; MBA or master's in innovation management preferred. Experience in project management, R&D, or strategic planning is advantageous.
- Chief Technology Officer (CTO)
- Responsibilities: Leads the company’s technological research and development (R&D), aligns technology-related decisions with the organization's goals, and explores new technological opportunities.
- Required Skills: Deep technical knowledge, strategic planning, leadership, and the ability to drive technology innovation.
- Education and Experience: Typically requires a degree in computer science, engineering, or related field, along with extensive experience in IT and technology development.
- Researcher
- Responsibilities: Conducts market and technology research to identify trends and opportunities, supports product development with factual insights.
- Required Skills: Analytical skills, proficiency in research methodologies, attention to detail.
- Education and Experience: Degree in market research, business, or a technical field. Experience in research roles within the industry.
- Product Manager
- Responsibilities: Manages the development and marketing strategy of products from conception through lifecycle management to ensure they meet customer needs and company goals.
- Required Skills: Product development, market analysis, customer engagement, cross-functional team leadership.
- Education and Experience: Bachelor’s degree in business, marketing, or related technical field, with experience in product development and management.
Types of Think Tanks for Advancing Innovation
- Strategic Innovation Team
- Composition: Management (and sometimes the board is invited as well).
- Focus: Developing long-term innovation strategies that align with the company's overarching goals, identifying new market opportunities, and ensuring the sustainability of innovation efforts.
- Optimal size: 5-15 people (pending on the management team size).
- Product and Service Innovation Team – for Idea Generation
- Composition: Marketing professionals, with some operational and/or technological people to confirm feasibility of ideas.
- Focus: Innovating around new or existing products and services to meet evolving market needs, improving customer experience, and ensuring the feasibility of ideas.
- Optimal size: 8-12 people (diversity in opinions and ideas, while still enabling efficient discussions)
- Technological Problem-Solving Team
- Composition: CEO, CTO/Operation, Marketing Manager, Innovation manager, and another manager from the marketing department.
- Focus: Internal screening, Idea bank management, execution and advancing specific project.
- Optimal size: 5 people (Internal screening and execution do not require a bigger team)
- Process Innovation Team
- Composition: Operations and process management experts./li>
- Focus: Streamlining and improving internal processes, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and implementing new tools and technologies to support operational excellence.
In conclusion, the formation and effective management of an Innovation Team are crucial for fostering a culture of continuous improvement and creativity within any organization. By assembling a diverse group of individuals equipped with the right skills, experience, and perspectives, and by clearly defining roles, responsibilities, and focus areas, organizations can significantly enhance their capacity for innovation.
Whether it's through generating groundbreaking ideas, developing and testing new products and services, conducting thorough market research, or managing projects efficiently, these teams are the driving force behind an organization's ability to innovate and stay competitive in the ever-evolving business landscape. Through strategic collaboration, continuous learning, and adaptation, Innovation Teams not only contribute to the immediate success of their projects but also lay the groundwork for long-term strategic growth and transformation.

Innovation Center
An "Innovation Center" can be both a physical location and a business unit within an organization, depending on how it is structured and its intended purpose:
- As a Physical Location: An Innovation Center can be a dedicated space designed to foster creativity and collaboration. It often features open work areas, labs for prototyping and testing, meeting rooms for brainstorming sessions, and technology-equipped spaces for research. This physical setup is intended to create an environment that stimulates innovative thinking and rapid development of ideas into tangible solutions.
- As a Business Unit: In a broader organizational context, an Innovation Center can refer to a business unit that is responsible for overseeing the innovation strategy across the company. This includes managing the innovation process, from idea generation through to commercialization, and may involve coordinating with various departments, external partners, and stakeholders. In this sense, the Innovation Center functions as the hub of innovation activities, regardless of where those activities physically take place within or outside the organization.
- As a blend of both: In many cases, organizations blend these two concepts, establishing an Innovation Center as both a physical space that encourages creative workflows and as a strategic unit tasked with driving the innovation agenda. This dual approach helps in aligning the physical and cultural aspects of innovation with the strategic and operational needs of the business.
Innovation Center Location
- Equipment and Furniture
- Flexible Workspaces: Modular furniture that can be easily reconfigured for workshops, brainstorming sessions, or individual work. This includes movable desks, chairs, and whiteboards.
- Prototyping Labs: Equipped with 3D printers, laser cutters, and other prototyping tools to quickly turn ideas into tangible models.
- High-Tech Meeting Rooms: Featuring advanced video conferencing technology to enable seamless collaboration with remote teams and partners.
- Relaxation and Creative Spaces: Areas with comfortable seating, perhaps even hammocks or bean bags, designed to stimulate creative thinking and provide a change of scenery.
- Innovation Library: A collection of books, journals, and digital resources covering topics from design thinking to technology trends, providing a wealth of knowledge for research and inspiration.
- Tech Hub: Access to high-speed internet, cloud computing resources, and a range of software tools for design, simulation, and project management.
- IT and Technology
- Collaboration Tools: Software that facilitates project management, idea sharing, and communication within the team and with external collaborators.
- Interactive Displays: Touchscreens and smart boards for interactive presentations and collaborative design sessions.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Equipment for exploring virtual prototypes, immersive learning, and creative visualization.
- Literature and Materials
- Innovation and Design Thinking Literature: A well-curated selection of books and publications on innovation methodologies, case studies, and success stories.
- Material Library: Samples of various materials that can be used in prototyping and design projects, providing a tactile resource for innovators.
- Games and Creative Stimuli
- Brainstorming Games: Games and puzzles that encourage lateral thinking and team bonding.
- Creative Prompts: Sets of cards or tools designed to spark new ideas or overcome creative blocks.
- Design and Zones
- Open Floor Plan: A spacious layout that encourages movement and interaction, with areas designated for different activities but no rigid separations, promoting a fluid and dynamic working environment.
- Collaboration Zones: Strategically placed to foster spontaneous discussions and idea exchanges.
- Quiet Zones: For deep thinking and concentration, away from the busier collaboration areas.
- Showcase Area: Where successful projects and innovations are displayed, inspiring the team and highlighting achievements.
- Size and Arrangement
- Size: The size of the Innovation Center should be proportional to the organization's size and the scope of its innovation activities. Ideally, it would be large enough to accommodate multiple teams and projects simultaneously, with enough flexibility to adapt to different working styles and needs.
- Arrangement: The arrangement should prioritize natural light, open spaces, and a visually stimulating environment, with a mix of modern and comfortable aesthetics to create an inspiring yet functional workspace.
Innovation Center UNIT
An Innovation Center UNIT is focused on fostering creativity and developing new ideas that can lead to significant business advancements. It operates as a semi-autonomous unit with the specific mandate to:
- Stimulate Creativity: Provide a space where creative thinking is encouraged and nurtured away from the constraints of day-to-day operations.
- Facilitate R&D: Concentrate on research and development activities to explore new technologies, methodologies, and business models.
- Prototype Development: Build and test prototypes rapidly, employing design thinking and agile methodologies to iterate quickly based on feedback.
- Collaboration and Networking: Act as a central point for collaboration with external entities, such as universities, research institutes, startups, and other partners that can contribute novel insights and technologies.
- Knowledge Sharing: Serve as a repository for best practices and lessons learned in innovation, disseminating this knowledge throughout the organization.
- Trend Analysis: Monitor and analyze emerging trends and disruptive technologies that could impact the industry and the business.
- Skill Development: Offer training and development programs to upskill employees in the latest innovation methodologies and technologies.
The presence of an Innovation Center is a strong indicator of a company’s commitment to staying ahead of the curve. It's a strategic investment in the future, serving as both a think tank and a laboratory for groundbreaking ideas.

Can Innovation Be a Core Strength of a Firm
Innovation can indeed be a core strength of a firm, and for many successful companies, it is a critical competitive advantage. To ensure that innovation is a core strength, firms should:
- Institutionalize Innovation: Embed innovation into the corporate culture and strategy. This means prioritizing innovation at the highest levels, from the CEO to the front-line employees.
- Invest in Innovation: Allocate sufficient resources—time, money, and people—to innovation activities. This includes investing in research and development (R&D) as well as innovation training programs.
- Encourage a Culture of Risk-Taking: Create an environment where calculated risks are encouraged and failure is seen as a learning opportunity, not a setback.
- Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration: Break down silos within the organization to encourage the free flow of ideas across different departments and teams.
- Leverage Customer Insights: Use customer feedback and insights to drive innovation, ensuring that new products and services meet actual market needs and preferences.
- Iterative Development: Employ agile and lean startup methodologies to develop and refine products and services rapidly based on real-world feedback.
- Attract and Retain Talent: Hire and retain individuals who are naturally curious and passionate about innovation. Provide them with opportunities for growth and development.
- Measure and Reward Innovation: Develop clear metrics for measuring innovation performance and reward contributions that drive the firm forward.
Innovation Leaders: Case Studies
A company with innovation as a core strength continuously evolves, stays relevant in the market, and can anticipate and respond to changes more effectively than competitors. Following are some case studies of companies that thrive on innovation and successfully nourish it as a culture.

Case Study 01: 3M
- Company: 3M, Maplewood, Minnesota, USA (founded in 1902)
- Overview: 3M, known for its culture of innovation, has a rich history of developing new products that span a variety of industries. From the Post-it Note to reflective road signs, 3M's innovations have often been the result of encouraging its employees to spend time on projects outside their primary responsibilities.
- Innovative Culture: 3M's "15% Time" policy allows employees to use up to 15% of their paid time to chase rainbows and hatch their own ideas. This policy has been a cornerstone of 3M's innovation culture, fostering an environment where creativity and experimentation are not just allowed but encouraged.
- Outcome: One of the most famous outcomes of this culture is the invention of the Post-it Note by Spencer Silver and Art Fry, a product that has become synonymous with quick, personal communication. This culture of innovation has helped 3M to sustain its growth, with thousands of products in its portfolio and a presence in various industries worldwide.

Case Study 02: Apple
- Company: Apple, Cupertino, California, USA (founded in 1976)
- Overview: Apple's innovation extends beyond its revolutionary products like the iPhone, iPad, and MacBook. The company's approach to design, marketing, and retail has also been groundbreaking. Apple's innovation culture is closely tied to its focus on design thinking and customer experience.
- Innovative Culture: Under the leadership of Steve Jobs and later on Tim Cook who replaced him, Apple has maintained a culture that prioritizes innovation at every level of product development and customer interaction. Apple's culture encourages thinking differently and pursuing engineering excellence, with a strong emphasis on design and usability.
- Outcome: Apple's approach has led to a series of industry-disrupting products that have set new standards in technology and design. Its relentless focus on innovation and the customer experience has made it one of the most valuable companies in the world, with a loyal customer base and strong market presence.

Case Study 03: Google (Alphabet)
- Company: Google (Alphabet), Mountain View, California , U.S. (founded in 1998)
- Overview: Google, now under its parent company Alphabet, is renowned for its innovative approaches not just in search technology but across a broad spectrum of industries, including advertising, mobile operating systems, and more recently, self-driving cars and health technology.
- Innovative Culture: Google's innovation culture is embodied in its famous "20% time" policy, which encourages employees to dedicate one day a week to side projects. This policy has spawned many of Google's products and services, including Gmail and Google News. Google fosters an open culture where ideas can come from anywhere, and failure is seen as a step towards innovation.
- Outcome: Google's commitment to innovation has kept it at the forefront of the technology industry, continuously expanding its product offerings and entering new markets. Its ability to innovate and adapt has solidified its position as a leader in multiple sectors, driving growth and maintaining a competitive edge.
These case studies showcase how fostering an innovative culture can lead to significant breakthroughs and sustained success in the business world. Each company, through its unique approach to encouraging creativity and experimentation among its employees, has managed to consistently introduce groundbreaking products and services that redefine markets.

Innovation Culture
An innovation culture is an organizational environment that nurtures unorthodox thinking and empowers employees to generate new ideas. This culture is fundamental to maintaining a competitive edge in today's fast-paced business world.
Key Elements in Supporting Innovation Culture
Here are some key attributes and actions that help cultivate an innovation culture:
- Leadership Support: Executives must champion innovation and lead by example, encouraging everyone to think differently.
- Open Communication: A free flow of ideas between all levels of staff, without fear of criticism or rejection, is essential.
- Risk Tolerance: The company must be willing to take calculated risks and accept that failure is often part of the innovation process.
- Resource Allocation: Investment in innovation, not just in R&D but across the organization, including time for exploration and creativity.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Breaking down silos and bringing diverse teams together to solve problems promotes a wider range of ideas and solutions.
- Continuous Learning: Providing opportunities for employees to learn and develop new skills keeps the organization ahead of emerging trends and technologies.
- Recognition and Rewards: Acknowledging and rewarding innovative efforts, even when they don’t lead to immediate success, reinforces a culture that values innovation.
An innovation culture is not something that can be implemented overnight. It requires a strategic approach and commitment at all levels of the organization to embed and sustain innovation as a core value.
Unusual Innovation Cultures
Following are some examples of companies that apply unusual work routines and rules, that successfully promote a culture of innovation:
 Valve Corporation:
Valve Corporation:
Valve, the video game developer and digital distribution company, known for titles like "Half-Life" and "Portal", operates on a "flat" organizational structure. The most distinctive feature is their "desk on wheels" policy. Employees can move their desks to any project area they are interested in working on, effectively choosing their own projects and teams. This unique approach encourages spontaneity, collaboration, and the free flow of ideas, embodying the company's belief that innovation stems from employees taking charge of their work and following their passions.
 Gore & Associates:
Gore & Associates:
W.L. Gore & Associates, a materials science company famous for its GORE-TEX® fabric, practices a lattice organizational structure instead of a traditional hierarchical model. There are no fixed job titles or chain of command. Employees, known as "associates," are encouraged to make commitments to projects that resonate with their skills and interests, similar to making commitments in a volunteer organization. This system fosters a strong culture of mentorship, experimentation, and direct communication, which has led to high levels of innovation and employee satisfaction.
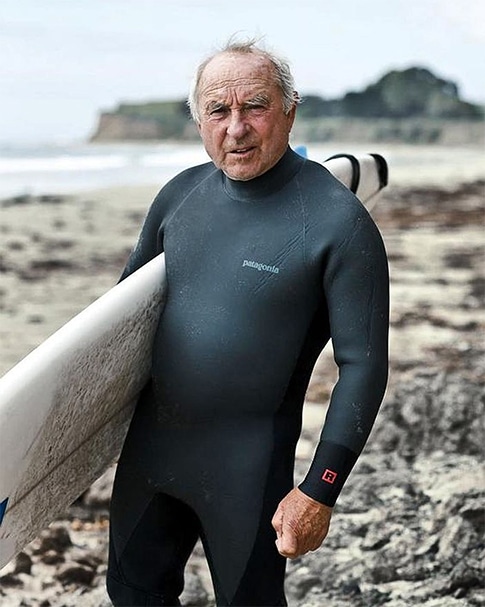 Patagonia:
Patagonia:
Patagonia, the outdoor clothing and gear company, is renowned not just for its commitment to environmental sustainability but also for its unconventional employee policies that support work-life balance and, indirectly, innovation. One of the standout policies is the "Let My People Go Surfing" rule, which allows employees to take breaks to go surfing (or participate in any other outdoor activity) when the conditions are perfect. This flexibility is designed to ensure that employees remain mentally and physically healthy, happy, and thus more creative and productive in their work. It underlines the company’s belief that a connection to nature fosters creativity and a passion for environmental stewardship, key elements in their innovative product designs.
In conclusion, fostering an innovation culture within an organization is a deliberate and ongoing effort that demands commitment from leadership and active participation from every employee. The examples of Valve Corporation, Gore & Associates, and Patagonia illustrate that unconventional work routines and rules can significantly contribute to nurturing this culture.
By placing trust in employees, allowing them to follow their passions, and providing an environment that supports work-life balance and cross-functional collaboration, companies can unlock a powerful source of creativity and innovation. These practices not only set these organizations apart in their respective industries but also serve as a testament to the potential of innovative cultures in driving sustainable business success.
As businesses continue to navigate an ever-changing landscape, embracing unique approaches to work and innovation may well be the key to unlocking new levels of growth and development.

When Innovation Thrives in an Organization
Innovation thrives in an organization when several key factors are aligned to create an ecosystem conducive to creative thought and its practical application. Here's what typically characterizes such an environment, alongside examples to demonstrate it:
Strategic Alignment
Innovation is aligned with the company's strategic goals, ensuring that efforts contribute meaningfully to the organization's direction.
- Canva (Founded in 2012) – This Australian-based startup has strategically aligned its innovation efforts with democratizing design, making it accessible to everyone from professionals to novices. By continuously enhancing its platform with user-friendly features and integrating market feedback into product development, Canva has emerged as a leading online design tool. This strategic alignment has propelled Canva from a niche startup to a global design powerhouse.
- Spotify (Founded in 2006) has masterfully aligned its innovation efforts with strategic goals, particularly in personalizing user experience through data analytics. This alignment has made Spotify a leader in streaming, adapting to changes in music consumption and user preferences.
Empowered Employees
Staff at all levels are empowered to challenge the status quo and are provided with the autonomy to pursue innovative ideas.
- Buffer (Founded in 2010) – Buffer, a social media management tool, takes employee empowerment to the next level with its transparency and autonomy principles. Employees have access to all company information, including salaries and financial status, and are encouraged to set their own schedules and work locations. This empowerment has fostered a culture of trust and innovation, leading to the development of new features and improvements based on employee initiatives.
- At Zappos (Founded in 1999), employees are empowered to deliver outstanding customer service, often in creative and unexpected ways. This empowerment is a cornerstone of their innovation in retail customer experience.
Collaborative Environment
Collaboration is encouraged across departments, fostering diverse perspectives and a holistic approach to innovation.
- Pixar Animation Studios fosters a collaborative environment through its open office layout and daily meetings where all employees, regardless of rank, are encouraged to provide feedback on projects. This culture of collaboration has contributed to its consistent production of hit films since the 1990s.
- Etsy (Founded in 2005), the online marketplace for handmade goods, fosters collaboration by connecting artisans with one another and with customers. This collaboration has driven innovation in how products are sold and presented online.
Supportive Infrastructure
There is an infrastructure in place that supports experimentation and rapid prototyping, enabling ideas to be developed and tested swiftly.
- Kickstarter (Launched in 2009) provides a platform and infrastructure that supports creators in bringing their innovative projects to life. By enabling rapid prototyping and feedback through crowdfunding, Kickstarter has become a hub for creative projects.
- Amazon's leadership in innovation is supported by its massive investment in infrastructure, such as AWS (Amazon Web Services), launched in 2006, which not only powers Amazon's vast e-commerce operations but also provides a platform for startups and established companies to scale their operations rapidly.
Adequate Resources
Necessary resources, including time, budget, and materials, are available to explore and implement new ideas.
- TransferWise (now Wise, Founded in 2011), a fintech company, has committed significant resources to innovation in the international money transfer market. By investing in technology that bypasses traditional banking systems to reduce fees and increase speed for cross-border transactions, Wise has challenged and innovated within the financial industry. The allocation of resources to technological development and customer experience has been crucial in its growth and success in disrupting the traditional banking sector.
- Patagonia (Founded in 1973), known for its commitment to sustainability, allocates resources to innovation in eco-friendly materials and supply chain transparency. This dedication supports their goal of reducing environmental impact.
Recognition of Effort
Innovation is recognized and celebrated, regardless of the outcome, which encourages ongoing engagement in innovative activities.
- Tata Group, one of India's largest conglomerates, hosts an annual Innovista program where it recognizes and celebrates innovative ideas and projects from its employees across the globe. This recognition fosters a culture of innovation within the company.
- Salesforce (Founded in 1999) has built a culture that celebrates innovation through its "Trailblazer" community and internal recognition programs. Celebrating innovation fosters a sense of ownership and pride among employees, encouraging continuous engagement in innovative activities.
Learning Culture
The organization promotes a culture of learning, where insights from both successes and failures are valued and shared.
- Dyson (Founded in 1991) epitomizes a learning culture, with its investment in the Dyson Institute of Engineering and Technology. The company not only innovates in product design but also invests in developing the next generation of engineers.
- SpaceX, led by Elon Musk, exemplifies a learning culture through its open acceptance of failures as a path to innovation. The company's transparent discussion about the causes of rocket launch failures, such as the Falcon 1 in 2006, and the subsequent iterations and improvements, illustrate how embracing failures can lead to historic successes, like the first privately funded spacecraft to reach the International Space Station in 2012.
In essence, the thriving of innovation within an organization is not by chance but by design. It requires a deliberate orchestration of elements such as strategic alignment, empowered employees, a collaborative environment, supportive infrastructure, adequate resources, recognition of efforts, and a robust learning culture. The examples of Canva, Spotify, Buffer, Zappos, Kickstarter, Wise, Patagonia, Tata Group, Salesforce, Dyson, and SpaceX demonstrate the diverse ways companies across industries and sizes can cultivate these elements to foster an ecosystem where innovation flourishes. These companies highlight that when an organization commits to embedding innovation into its DNA, the potential for transformative growth and impact is boundless.

When Innovations Meet Institutions
Institutions (such as governmental bodies, regulatory agencies, educational systems, financial organizations, healthcare facilities, and traditional corporate enterprises) represent the established structures, norms, and practices that govern, support, or influence society functions. When innovations meet these entities, the interaction can lead to significant changes in how these institutions operate, adapt, and serve their purposes. The potential implications and transformations are multifaceted.
Innovation Impact Accross Sectors
- Governmental and Regulatory Bodies: Innovation can lead to the creation of new policies, regulations, or governmental initiatives aimed at fostering further innovation, addressing emerging technological challenges, or protecting consumers and citizens. For example, the advent of digital currencies has prompted governments worldwide to explore regulations and frameworks for crypto currencies.
- Educational Systems: Innovations in technology and pedagogy can transform educational institutions by introducing new learning models, such as online courses, virtual classrooms, and interactive learning platforms, thereby expanding access to education and tailoring learning experiences to individual needs.
- Financial Organizations: Fintech innovations challenge traditional banking and financial services, leading to more inclusive financial systems, improved customer experiences, and the emergence of new services like mobile payments, peer-to-peer lending, and blockchain-based transactions.
- Healthcare Facilities: In the healthcare sector, innovations in medical technology, telehealth, and patient data management can revolutionize patient care, improve outcomes, and make healthcare more accessible and efficient.
- Corporate Enterprises: Within traditional corporations, innovation can disrupt standard business models and operational processes, prompting a shift towards more agile, sustainable, and customer-centered practices.
Each of these interactions between innovations and institutions not only changes the institutions themselves but also has the potential to impact society at large, driving progress, improving quality of life, and solving complex challenges.

How Can Innovation Be Promoted in an Organization
Promoting innovation within an organization involves creating an environment that nurtures creative thinking and the practical implementation of new ideas. Here are effective strategies to achieve this:
- Leadership Commitment: Leaders should visibly support and participate in innovation initiatives, setting a tone that values creativity and experimentation.
- Resource Allocation: Dedicate resources specifically for innovation activities, including budget, time, and tools, to explore new ideas.
- Innovation Infrastructure: Establish structures that support innovation, such as innovation labs, cross-functional teams, and platforms for idea sharing.
- Employee Empowerment: Empower employees at all levels to contribute ideas and take ownership of innovation projects.
- Training and Development: Offer training programs that enhance skills in creative thinking, problem-solving, and project management.
- Reward and Recognition: Implement a system to reward innovative ideas and efforts, even if they don’t all succeed, to encourage ongoing participation.
- Foster Collaboration: Promote collaboration within and outside the organization to bring in diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Cultivate a Fail-forward Culture: Create a culture where failure is seen as a learning opportunity, not a setback.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can promote a culture of innovation that continuously seeks to improve, adapt, and evolve. Following we describe how to do it
Actionable Step-by-Step Plan for Promoting Innovation
- Assess Current State: Evaluate your organization's current innovation culture. Identify barriers to innovation and areas for improvement.
- Gain Leadership Buy-In: Present the benefits of fostering an innovation culture to leadership. Secure commitment and resources for innovation initiatives.
- Develop an Innovation Strategy: Outline clear goals for what you aim to achieve through innovation. This could include product development, process improvement, or entering new markets.
- Establish an Innovation Infrastructure: Set up structures to support innovation, such as dedicated innovation teams, innovation labs, or online platforms for idea submission and collaboration.
- Launch Training Programs: Organize workshops and training sessions focused on creative thinking, design thinking, and other relevant skills to empower employees.
- Create a Rewards System: Design a recognition and rewards program for employees who contribute innovative ideas or lead successful innovation projects.
- Promote Cross-functional Collaboration: Encourage teams from different departments to work together on innovation projects. This can be facilitated through regular innovation challenges or hackathons.
- Implement a Fail-forward Culture: Share stories of both successes and failures in innovation efforts, highlighting what was learned. Ensure that the organization supports experimentation and risk-taking.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review the progress of your innovation initiatives. Be prepared to adjust your strategy and tactics based on feedback and outcomes.
 Case Study: Philips
Case Study: Philips
- Background: Philips, a global leader in healthcare, lifestyle, and lighting, recognized the need to transform into a more innovative organization to remain competitive and address rapidly changing market demands.
- What Was Done:
- Leadership Commitment: Philips' leadership committed to innovation as a core value. They lead by example, actively participating in innovation initiatives and providing the necessary resources.
- Innovation Infrastructure: Philips established its "Innovation Hubs" around the world. These hubs serve as centers for research and development, bringing together experts from various fields to collaborate on innovative solutions.
- Employee Empowerment and Collaboration: Philips launched the "Accelerate!" program, encouraging employees to contribute ideas and collaborate across functions. This program aimed to increase agility, customer focus, and entrepreneurial culture within the company.
- Results/Impact: Through these strategies, Philips successfully transformed its organizational culture to one that prioritizes innovation. This shift helped Philips to accelerate product development, improve operational efficiency, and enter new markets. Notably, Philips' focus on healthcare innovation, which resulted inventions such as a Portable X-ray and Ultrasound Systems, HeartStart Automated External Defibrillator, IntelliVue Patient Monitoring Systems and SkinCare Assessment Device, has positioned it as a leader in health technology, demonstrating the power of innovation to drive corporate transformation and industry leadership.
In summarizing the journey to foster innovation within an organization, it is evident that a strategic, holistic approach is essential. From gaining leadership buy-in and dedicating resources to empowering employees and fostering a fail-forward culture, each step builds towards creating a dynamic environment where innovation can flourish.
The case of Philips serves as a powerful testament to the transformative impact of embedding innovation into the organizational fabric. By systematically implementing these strategies, any organization can set the stage for continuous improvement, adaptation, and evolution, ensuring they not only keep pace with but lead in an ever-changing global landscape.

What Kills Innovation
Several factors can stifle innovation within organizations, turning vibrant ideas into missed opportunities. Recognizing and addressing these innovation killers is crucial for fostering a culture of creativity and growth.
Common Innovation Killer
- Fear of Failure: A culture that punishes failure creates an environment where employees are afraid to take risks or propose new ideas.
- Lack of Support: Without leadership support and adequate resources, innovative projects can struggle to get off the ground.
- Overemphasis on Processes: While processes are important, too much bureaucracy can slow down or completely halt the innovation process.
- Short-term Focus: Prioritizing short-term gains over long-term innovation can prevent the development of groundbreaking ideas that require time to mature.
- Isolation: Operating in silos, without cross-departmental collaboration, limits the exchange of ideas and perspectives necessary for innovation.
- Resistance to Change: An organizational culture resistant to change is likely to reject new ideas before they have a chance to prove their value.
- Lack of Diversity: A lack of diversity in teams can lead to homogenous thinking, reducing the breadth of ideas and solutions considered.
- Inadequate Reward Systems: Failing to recognize and reward innovative efforts can demotivate employees from pursuing creative endeavors.
Addressing these barriers is essential for any organization aiming to harness the full potential of its people and cultivate a thriving innovation ecosystem. Following we describe how it can be done.
How to Address Innovation Killers
- Fear of Failure: Cultivate a fail-forward culture where mistakes are viewed as learning opportunities. Encourage experimentation by setting aside specific resources for high-risk, high-reward projects.
- Lack of Support: Secure leadership commitment by demonstrating the potential ROI of innovation initiatives. Create innovation task forces that include members of the leadership team. Apply Mentorship programs.
- Overemphasis on Processes: Streamline processes by adopting agile methodologies that prioritize flexibility and rapid iteration. Establish a balance between necessary governance and creative freedom.
- Short-term Focus: Set clear long-term innovation goals and incorporate them into the strategic planning process. Allocate a portion of the budget to projects with longer timelines.
- Isolation: Foster cross-functional collaboration through regular innovation workshops, mixed departmental teams and collaboration awards. Utilize digital collaboration tools to facilitate communication across silos.
- Resistance to Change: Implement change management practices that include transparent communication, change ambassadors, training, and involvement of employees in the change process to reduce resistance.
- Lack of Diversity: Actively recruit and promote individuals from diverse backgrounds, disciplines, and perspectives. Encourage diverse teams to tackle innovation challenges.
- Inadequate Reward Systems: Develop a comprehensive rewards system that recognizes both successful outcomes and valuable learning from failed projects. Include non-monetary rewards such as recognition and opportunities for professional growth.

Case Study: Kodak
- Background:
- Kodak, once a dominant force in photography, failed to adapt to the digital revolution.
- Despite inventing the first digital camera in 1975, Kodak was reluctant to shift its focus away from film because of its profitable film business.
- Barriers Encountered:
- Fear of Failure: Kodak's leadership was afraid that embracing digital technology would cannibalize its film business.
- ILack of Support: The digital photography division did not receive the support and resources it needed to innovate and compete effectively.
- Short-term Focus: Kodak prioritized immediate profits from film sales over the long-term potential of digital photography.
- Results/Impact: Kodak's inability to overcome these barriers led to a decline in its market share and relevance. The company filed for bankruptcy in 2012, becoming a cautionary tale of how fear of failure, lack of support, and a short-term focus can kill innovation and lead to the downfall of even the most established organizations.
Addressing the barriers to innovation requires a strategic approach and commitment at all levels of the organization. By learning from failure cases like Kodak, companies can better navigate the challenges of fostering an innovative culture.
Innovation and its Enemies
Innovation often faces resistance not just internally within organizations but also from external forces. Identifying and understanding these "enemies" of innovation can help in strategizing to overcome them:
- Status Quo Bias: Both individuals and institutions may prefer existing conditions due to the comfort and predictability they offer, resisting changes innovation brings.
- Fear of failure, as well as fear of success, can both be attributed to a desire to keep the status quo as is.
- Fear of failure, as well as fear of success, can both be attributed to a desire to keep the status quo as is.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Overly stringent regulations can stifle innovation by creating barriers to entry for new ideas and technologies, especially in highly regulated industries.
- One of our clients, a pharma company, was reluctant to ask the health authorities if they could register a prescription drug for children as an over-the-counter (less regulated) drug for adults. When we advised them to try, they were surprised to learn that the health ministry approved their request!
- One of our clients, a pharma company, was reluctant to ask the health authorities if they could register a prescription drug for children as an over-the-counter (less regulated) drug for adults. When we advised them to try, they were surprised to learn that the health ministry approved their request!
- Market Inertia: Established markets may resist innovation due to entrenched interests, legacy systems, and the fear of cannibalizing existing products.
- Hospitals and doctors in some countries still insist on using film (slide) output for scans, instead of digital files. Film manufacturers ceased to produce films for imaging, yet the customers refuse to go digital.
- Hospitals and doctors in some countries still insist on using film (slide) output for scans, instead of digital files. Film manufacturers ceased to produce films for imaging, yet the customers refuse to go digital.
- Risk Aversion: Investors and stakeholders often favor safe, short-term gains over potentially risky, long-term innovations.
- Pharmaceutical companies prefer to extend their patents by introducing minor derivatives to their original formulas, rather than risk it with developing new molecules.
- Pharmaceutical companies prefer to extend their patents by introducing minor derivatives to their original formulas, rather than risk it with developing new molecules.
- Limited Vision: A lack of foresight or understanding of emerging trends can lead organizations to dismiss innovative ideas that don't fit within their current paradigm.
- It took Microsoft several years to embark on the internet “wagon,” which served competitors well.
- It took Microsoft several years to embark on the internet “wagon,” which served competitors well.
- “Not Invented Here” Syndrome: Some organizations dismiss innovations simply because they originate externally, missing out on valuable opportunities for growth and improvement.
- Nokia in the early 2000s dismissed the potential of touchscreen smartphones, focusing instead on its traditional keyboard phones. This decision overlooked external innovations in smartphone technology, notably the introduction of Apple's iPhone in 2007, leading to Nokia's significant loss in market share in the following years
- Nokia in the early 2000s dismissed the potential of touchscreen smartphones, focusing instead on its traditional keyboard phones. This decision overlooked external innovations in smartphone technology, notably the introduction of Apple's iPhone in 2007, leading to Nokia's significant loss in market share in the following years
- Resource Constraints: Insufficient funding, time, or talent dedicated to exploring and implementing new ideas can significantly hamper innovation efforts.
- Tesla faced resource constraints in its early years, particularly around 2008, when it struggled to secure funding for production of the Tesla Roadster, risking the company's ability to innovate and nearly leading to bankruptcy before securing essential investments and loans.
- Tesla faced resource constraints in its early years, particularly around 2008, when it struggled to secure funding for production of the Tesla Roadster, risking the company's ability to innovate and nearly leading to bankruptcy before securing essential investments and loans.
Overcoming these innovation enemies requires a strategic approach that includes fostering a culture of openness, continuously scanning the external environment for changes, encouraging risk-taking within reasonable boundaries, and actively seeking collaboration and partnerships.

Innovation Jobs
The innovation landscape has created a diverse range of job opportunities focused on driving and managing change across various industries. Innovation jobs are characterized by roles that demand creativity, strategic thinking, and a passion for breaking new ground.
Common Innovation Positions
- Innovation Manager: Leads and manages the company's innovation efforts, overseeing the development of new products or services and fostering a culture of innovation within the organization.
- Product Developer: Works on the creation and development of new products, from conceptualization to launch, ensuring they meet market needs and consumer preferences.
- R&D Scientist/Engineer: Engages in research and development activities to discover new technologies or refine existing ones, contributing to the company's innovative capabilities.
- UX/UI Designer: Focuses on designing user experiences and interfaces that are intuitive and innovative, enhancing user engagement with products or services.
- Data Scientist: Utilizes big data and analytics to uncover insights that can lead to innovative solutions and strategies for the company.
- Innovation Consultant: Advises organizations on creating and implementing innovation strategies, helping them stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
- Chief Innovation Officer (CINO): A senior-level role responsible for setting the organization's innovation agenda and ensuring alignment with overall business objectives.
Innovation jobs are not confined to tech companies; they are increasingly common in traditional sectors such as healthcare, finance, education, and government, reflecting the universal importance of innovation across all areas of the economy.

Innovation Jobs Near Me
Finding innovation-related jobs in your area can be an exciting opportunity to engage in creative and transformative work. Here are some tips and resources to help you locate innovation jobs nearby.
- Online Job Portals: Websites like Indeed, LinkedIn, Glassdoor, and Monster allow you to search for jobs by keyword and location. Use terms like "innovation," "product development," or specific titles such as "Innovation Manager" to find relevant listings.
- Company Websites: Many companies post job openings on their own websites. Identify organizations known for their innovative culture or those with dedicated innovation departments and check their careers page regularly.
- Networking: Attend industry meetups, conferences, and seminars related to innovation. Networking with professionals in the field can provide insider information on job openings and referrals.
- Innovation Hubs and Incubators: Innovation hubs, incubators, and accelerators often host companies and startups focused on innovation. They may have job boards or connections to companies looking for innovative talent.
- Recruitment Agencies: Some agencies specialize in placing candidates in creative, tech, and innovation roles. Registering with these agencies can provide access to unadvertised opportunities.
- Social Media: Follow companies, innovation leaders, and industry groups on social media platforms. They often share job openings, insights, and updates on new projects that could lead to job opportunities.
Remember, innovation jobs aren't limited to tech startups; they're found across all sectors. Tailoring your search to your interests and industry can help you find a role that's right for you.

Innovation to Transform Education Training
Innovation plays a critical role in transforming organizational education and training, making learning more accessible, engaging, and effective. Here are keyways innovation is reshaping the educational landscape:
- E-Learning Platforms: Online learning platforms offer flexible, self-paced learning opportunities that can be tailored to individual needs, breaking geographical barriers to education.
- Gamification: Incorporating game design elements into education increases engagement and motivation, making learning more interactive and enjoyable.
- Adaptive Learning Technologies: These technologies adjust the content and pace of learning based on the learner's performance, providing personalized learning experiences.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR can simulate real-world environments for immersive learning experiences, particularly useful in fields requiring hands-on training.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education: AI can automate administrative tasks for educators, provide tutoring and support for students, and offer insights into learning patterns to improve educational outcomes.
- Blockchain for Education: Blockchain technology can securely store educational records, making it easier to verify qualifications and share credentials between institutions.
- Collaborative Learning Tools: Tools like online forums, video conferencing, and shared digital workspaces facilitate collaboration among students and teachers, regardless of location.
Innovations in education and training are not only improving the delivery of organizational education but also preparing learners for a future where adaptability and lifelong learning are key.

Innovation Can Be Increased by
Enhancing an organization's innovative capacity involves several strategic actions and cultural shifts. Here are effective ways to increase innovation:
- Fostering a Culture of Creativity: Create an environment where new ideas are welcomed, and employees feel safe expressing their thoughts and taking risks.
- Encouraging Collaboration: Promote teamwork across different departments and disciplines to combine diverse perspectives and expertise, sparking innovative solutions.
- Implementing Idea Management Systems: Use digital platforms to collect, evaluate, and track ideas efficiently, ensuring that valuable insights are not overlooked.
- Investing in Continuous Learning: Provide opportunities for employees to acquire new skills and knowledge, keeping the organization at the forefront of industry trends and technologies.
- Empowering Employees: Give individuals autonomy and ownership over projects, empowering them to pursue innovative solutions.
- Rewarding Innovation: Recognize and reward efforts and achievements in innovation, reinforcing its value to the organization.
- Leveraging Customer Insights: Engage with customers to understand their needs and challenges, using this feedback as a source of innovation inspiration.
- Adopting Agile Methodologies: Implement flexible and adaptive project management practices that allow for quick iteration and responsiveness to change.
- Creating Innovation Spaces: Designate physical or virtual spaces dedicated to brainstorming and collaborative work, stimulating creative thinking.
- Establishing Partnerships: Collaborate with universities, startups, and other organizations to gain fresh insights and access to new technologies.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can cultivate an environment that not only supports innovation but actively drives it, leading to sustained growth and competitiveness.

Innovation Council
An Innovation Council is a strategic group within an organization tasked with fostering a culture of innovation and guiding the innovation process. It typically comprises senior leaders and key stakeholders from various departments who bring diverse perspectives and expertise.
The main functions and benefits of establishing an Innovation Council include:
- Strategic Oversight: Provides governance and strategic direction for innovation initiatives, ensuring alignment with organizational goals.
- Resource Allocation: Decides on the allocation of resources to innovation projects, balancing the portfolio between short-term gains and long-term transformative projects.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration across departments, breaking down silos and promoting a unified approach to innovation.
- Idea Evaluation and Selection: Oversees the evaluation of new ideas and selects those with the highest potential for development and implementation.
- Policy and Process Development: Establishes policies and processes that support innovation, including idea submission protocols, evaluation criteria, and project management methodologies.
- Culture and Engagement: Champions a culture of innovation within the organization, encouraging participation and engagement from all employees.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Tracks the progress of innovation projects and reports on outcomes, learning, and impact to stakeholders.
By providing leadership and structure, an Innovation Council can play a pivotal role in driving an organization’s innovation agenda, ensuring that efforts are focused, efficient, and aligned with strategic objectives.

What are the 4 C's of Innovation?
The 4 C's of innovation are a framework that outlines the key components necessary for fostering a culture of innovation within organizations or teams. These components are:
- Curiosity: Encourages asking questions, exploring new possibilities, and seeking out new knowledge. Curiosity drives the desire to understand how things work and how they can be improved.
- Creativity: The ability to think outside the box and come up with novel ideas or solutions. Creativity involves connecting disparate ideas, reimagining existing processes, and envisioning new ways to address challenges.
- Collaboration: Recognizes that the best ideas often come from the combination of diverse perspectives. Collaboration involves teamwork, open communication, and the sharing of ideas and resources to achieve common goals.
- Courage: The willingness to take risks and the resilience to face failure. Innovation involves experimenting with new ideas, which requires courage to challenge the status quo and persistence to continue exploring solutions despite setbacks.
Together, these 4 C's create an environment where innovation can thrive. They emphasize the importance of a supportive culture that values inquisitiveness, imagination, teamwork, and bravery in the pursuit of novel solutions and breakthroughs.
Systematic innovation
Interested in getting help with systematic innovation processes and developing new products and services?
Contact us: [email protected] ,+972-9-958-5085
Innovation Articles
- Innovation - overview
- Innovation management and process
- Innovation tools and methods
- Innovation and other disciplines
- Innovation in organizations
- Innovation importance and goals
- Innovation values and inspiration
- Innovation education and career
- Product and service innovation
- Technological innovation
- Innovation examples
- Innovations across various industries
- Innovation terms (glossary)





